
Proxy is an intermediary server that plays a crucial role in network communication. It sits between the user and the target server, receiving user requests and forwarding them to the target server, thereby hiding the user’s real IP address and ensuring anonymity and privacy. The use of proxies is not limited to data collection; it is widely employed in bypassing geographical restrictions, improving network security, enhancing anonymity, and many other fields. Understanding the working principles of proxies and the different types of proxies can help users choose the most suitable proxy service to optimize their network experience.
A proxy is an intermediary server that sits between the user and the target server. Its main function is to receive user requests, forward them to the target server, and then return the server’s response to the user. Proxies not only hide the user’s real IP address but can also process or modify the data during the request and response process.
When a user tries to access a website or service, the browser (or other application) sends a request to the target website. The request is first sent through the proxy server, which processes the request and sends it to the target server. At this point, the target server sees the proxy server’s IP address instead of the user’s real IP. The server then processes the request and sends the response data back to the proxy server, which forwards it to the user.
For example, if you want to access a blocked website like YouTube, without a proxy, direct access will be restricted. But if you use a proxy server, YouTube will treat the request as coming from a regular user, thus allowing access without blocking it.
There are many types of proxies, each serving different purposes and use cases. Common types of proxies include:
HTTP Proxy: Supports only the HTTP protocol, meaning it handles requests for web pages accessed through browsers or applications. It is commonly used for web browsing, website data scraping, SEO optimization, and ad analysis. HTTP proxies are typically used for web requests.
SOCKS5 Proxy: Supports multiple protocols. In addition to HTTP, it can handle FTP, SMTP, POP3, and other network protocols. SOCKS5 is a more universal proxy protocol suitable for any TCP/IP-based application. It is ideal for P2P file sharing, online gaming, video streaming, and various network applications. For example, if you are using BT download, email clients, or remote desktop (RDP), SOCKS5 is more appropriate.
Transparent Proxy: A “stealth” proxy that users typically do not notice when accessing the web. It is mainly used for network management, traffic monitoring, content filtering, and caching acceleration. While it effectively manages network traffic, it does not provide privacy protection or encryption, so it is not suitable for protecting user anonymity or privacy. If you need to hide your real IP address or enhance privacy, a transparent proxy might not be the best choice.
Anonymous Proxy: Can hide the user’s real IP address but reveals itself as a proxy server in the request. This means that although the target website cannot see the user’s real IP, it can detect that the request is coming from a proxy server.
High Anonymity Proxy (Elite Proxy): Not only hides the user’s real IP address but also conceals the fact that it is a proxy server. In other words, the target website cannot see the real IP address of the user and cannot detect that the request is coming through a proxy server. This type of proxy provides a higher level of anonymity protection.
Bypassing Geographical Restrictions: Some websites or platforms restrict access to content based on the user’s IP address. Proxies can help bypass these geographical blocks. For example, many video streaming platforms, news websites, and e-commerce platforms offer different content or prices to users in different regions. With a proxy, you can access this content via IPs located in different countries.
Avoiding IP Bans: Large-scale data collection (such as web scraping) can trigger anti-bot mechanisms on websites, resulting in IP bans. By using multiple proxy IPs and rotating proxy pools, you can avoid using the same IP frequently, reducing the risk of being banned. For instance, when scraping product information from e-commerce websites, rotating IPs in a proxy pool can prevent the website from detecting too many requests and blocking your IP.
Improving Data Scraping Efficiency: Proxies can speed up the data scraping process, especially when multiple proxies work simultaneously, sharing different request tasks. For example, multiple web pages or API interfaces can be accessed at the same time, improving scraping efficiency.
Increasing Privacy and Anonymity: Using proxies effectively hides the real IP address, protecting the privacy of the scraping activity. This is especially important for users who don’t want their data collection activities exposed or tracked. When scraping social media data, proxies help hide the real IP address, preventing detection and account bans by the platform.
In addition to being widely used for data collection, proxies have many other applications:
Network Security: By hiding the real IP address, proxies can help avoid DDoS attacks and other network threats. When performing sensitive actions (such as accessing bank accounts or logging into corporate systems), proxies enhance privacy protection and avoid data leaks.
Anonymous Access: Proxies help users bypass geographical or IP restrictions to access blocked content. By using proxies, users can hide their location, device information, and other personal details that might expose their identity, thereby enhancing online anonymity.
Load Balancing: Proxies can distribute traffic across multiple servers, optimizing network load and ensuring stable services.
Bandwidth Control: Proxies can be used to limit specific types of data transmission to manage network bandwidth.
Buying Hot Products: Proxies can help users bypass regional restrictions or purchasing limits on e-commerce platforms to purchase limited products or participate in promotions specific to certain regions.
Configuring a proxy is simple. Taking Cliproxy as an example, you can choose from two types of proxy plans: Socks5 and Residential proxies. You can select the one that fits your needs.
Socks5 proxies are sold by IP and support various usage methods such as account password authentication and client extraction. It’s recommended to use a Windows desktop application, which is simple to operate for setting up IP proxies.
IP proxies often need to be used in conjunction with a browser, fingerprint browser, or third-party application.
Cliproxy’s Windows app allows filtering IPs by various conditions, including country, state, city, postal code, and operator. Simply choose a suitable IP and right-click to forward the port, and you can configure it on the corresponding port.
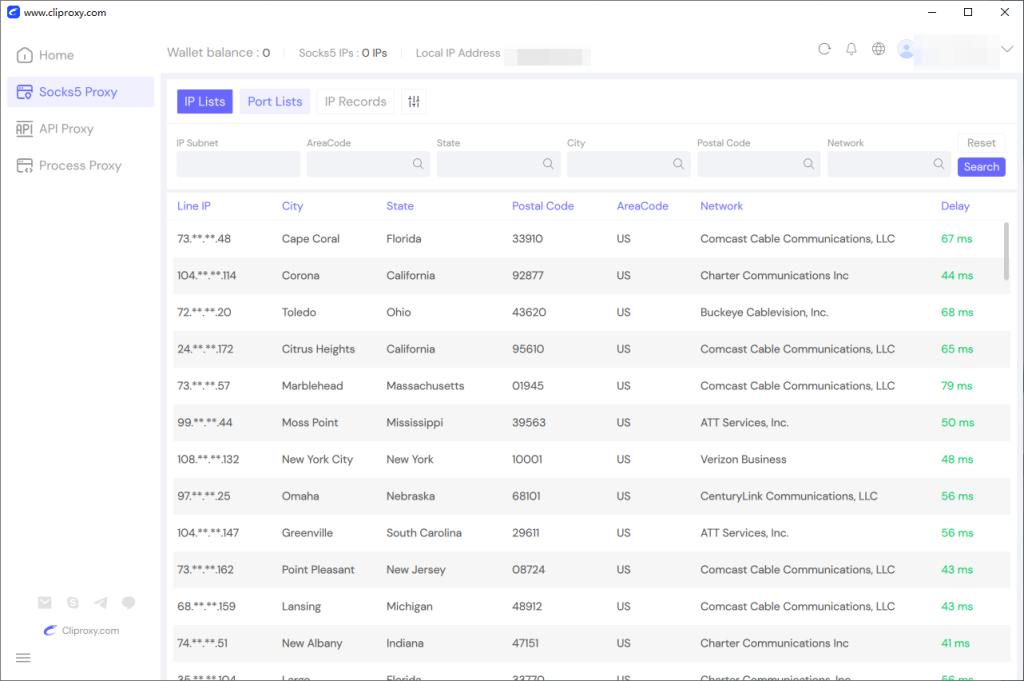
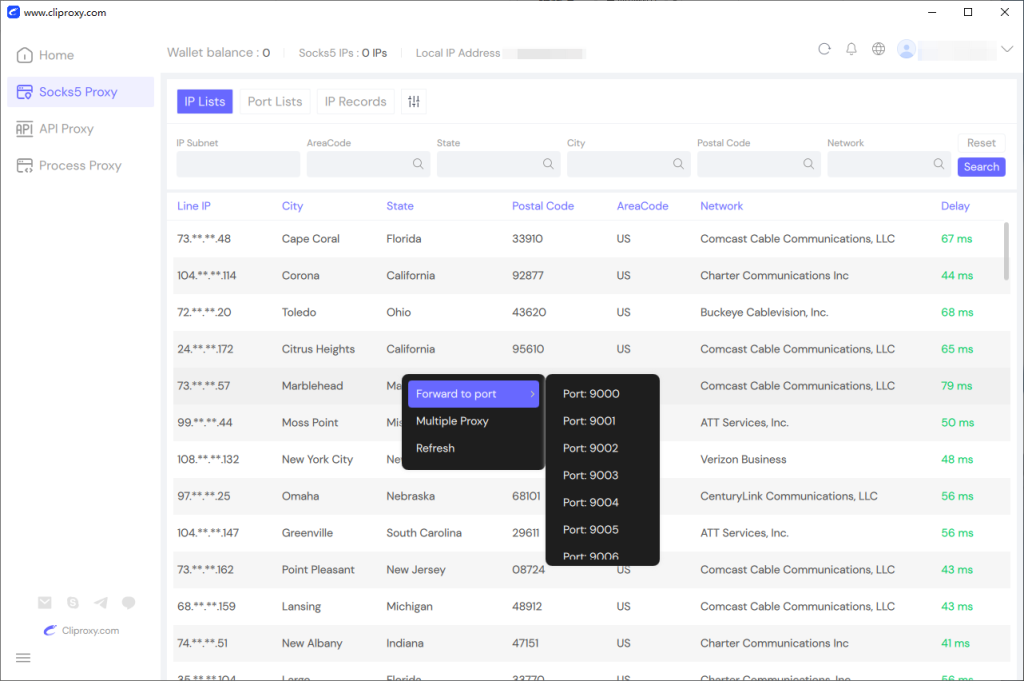
In the forwarding list, copy the IP and port and paste it into the browser’s corresponding proxy settings to achieve proxy functionality.
To verify if the proxy is working, you can visit IP detection websites to check if the real IP is hidden. After setting up the proxy, you can visit websites like ipip.net or whoer.com to check whether the IP is successfully proxied.
Regularly Rotate Proxies: Use multiple proxy IP addresses to avoid having a single IP blocked or restricted.
Set Reasonable Request Intervals: Avoid making requests too frequently to reduce the risk of detection and blocking.
Use High Anonymity Proxies: Enhance privacy and security by avoiding exposure of proxy server information. Choose a reliable residential proxy service provider.
Manage Proxies Using a Proxy Pool: Build a proxy pool and dynamically select suitable proxies to increase the success rate of scraping.
Can proxies be used for social media platform data scraping?
Yes, proxies are widely used for data scraping on social media platforms. They help users bypass IP blocks and restrictions, improving the success rate of data scraping. However, when scraping social media data, it’s important to follow the platform’s API usage policies and legal regulations.
Can free proxies be used for data collection?
While free proxies can be used for simple data collection, they usually pose security risks (such as data leaks or malware). Free proxies tend to be slower, less stable, and are often blocked quickly. For long-term and efficient data scraping, it is recommended to use paid proxy services.
What is a Data Proxy?
A Data Proxy is an intermediary server or service that routes client requests to the target server. It acts as a gateway, typically used to hide the user’s real IP address and obscure their identity. Data proxies are commonly used in web scraping, bypassing content restrictions, or ensuring anonymity.
How do website detect multiple accounts?
Websites detect multiple accounts by monitoring several factors. First, if multiple accounts are created from the same IP address, it may raise suspicion. Websites can also track unique browser fingerprints (such as cookies and device information). Additionally, user activity patterns (login times, purchase history, interaction behaviors) are analyzed to spot abnormal behavior. Lastly, websites may trigger CAPTCHA verification for users creating multiple accounts in a short period.
The application of proxies in various scenarios demonstrates their powerful functionality and versatility. Whether for data collection, enhancing online privacy protection, bypassing geographical blocks, or improving network security, proxies provide robust support to users. By properly configuring proxies and using efficient scraping techniques, users can protect their privacy and perform tasks efficiently and reliably. However, it is crucial to choose secure and reliable services to avoid security risks and bans caused by improper use of proxies.


